Mohno PumpsStructure and Principle
Principles of Mohno Pumps
Mohno Pumps are progressing cavity pumps that enable non-pulsating, metered conveyance.
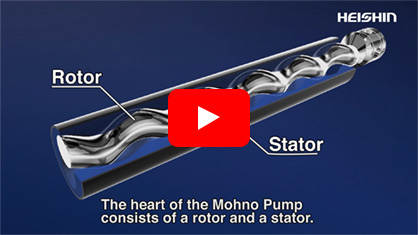
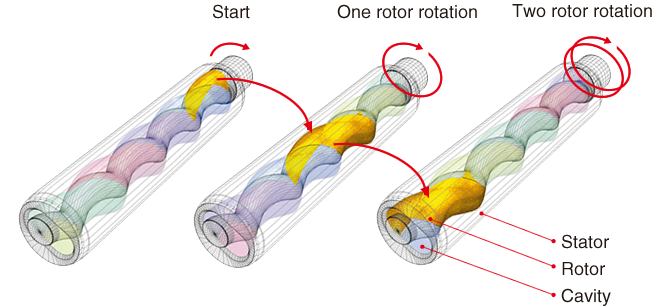
The heart of the Mohno Pump consists of a rotor, which functions as a male screw, and a stator, which functions as a female screw. When the rotor is inserted into the stator, sealed chambers called "cavities" are created in the gaps. The rotation of the rotor inside the stator generates strong suction that can draw in even high-viscosity fluids while forming new cavities that move toward the discharge outlet. Fluids drawn into the cavities are continuously conveyed forward with the movement.
The cross-sectional area of the cavities is always constant at any rotor position, which ensures a consistent conveyance flow.The flow rate is directly directly proportional to the rotor's rotational speed. Reversing the rotor's rotational direction can switch the direction of the suction/discharge.
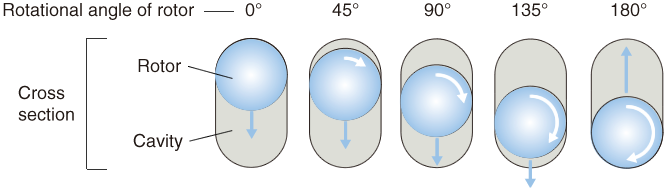
At any cross-section perpendicular to the shaft, the cross-sectional area of the cavities created by the rotor and the stator is always constant,enabling non-pulsating, metered conveyance.
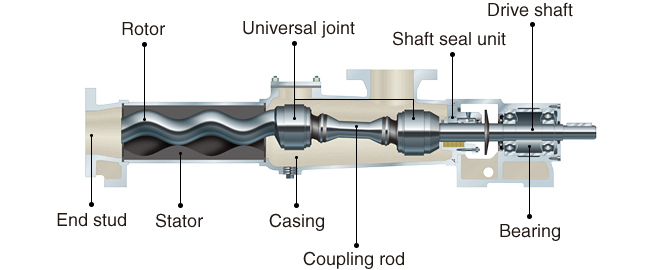
Structure of Mohno Pumps
Rotor
Mohno Pump's rotor is composed of a single-threaded male screw and can be made of various materials to suit the application.
- Materials
- Various stainless steels, alloy tool steel, titanium, Hastelloy®, Carpenter, alumina (Al₂O₃), etc.
* Application of various surface treatments are also possible.
Stator
The stator is composed of a double-threaded female screw with an elastic body and an outer tubing. The stator can be made of various materials such as plastic or metal to suit the application.
- Materials
- NBR, EPDM, FKM, FFKM, VMQ, AU, PTFE, etc.
* Hastelloy® is a registered trademark of Haynes International, Inc.